Authors
Published
8 Dec 2021Form Number
LP1537PDF size
8 pages, 5.8 MBAbstract
The city of Barcelona has set an ambitious plan for digital transformation that will place the city in the cutting edge of efficiency, transparency, and social innovation. Using the latest edge technologies from Lenovo, Barcelona is implementing data-driven, smart city technologies to improve its services and the quality of life for its citizens. Learn how Barcelona is implementing these technologies, what are the benefits of this kind of initiative and how Barcelona is becoming a smart city.
What makes a smart city “smart”
With more and more of the world’s population moving to urban areas, many challenges, such as improving safety, transportation and mitigating pollution, are increasing. Smart cities use intelligent solutions to optimize municipal infrastructure and smart responsive governance to engage citizens, enterprises and public entities in the management of their city. A system of sensors, networks, and applications collect useful data, like traffic congestion, energy use, and CO2 levels to improve the day to day life and deliver a much better “ experience”.

Though the term “smart cities” is new, the idea isn’t. Ancient Roman cities used elements of the concept, such as the technology to make their citizens’ lives easier. Aqueducts and water drainage systems are just two ways they did that.
The main goals of a smart city are to improve policy efficiency, reduce waste, pollution and inconvenience, improve social and economic quality, and maximize social inclusion.
Well-designed Edge, 5G and IoT infrastructures can also leverage benefits such as traffic management to reduce congestion and recognize pedestrian patterns. This can also apply to building management systems that must provide an environment that keeps occupants safe and buildings operating efficiently. Smart IT infrastructure helps city managers plan around events or improve response to disasters and emergencies.
As these requirements continue to grow, city managers will need to expand existing IT systems. A scalable solution allows for additional applications to be added such as electronic signage, access controls, crowd and traffic management, or allowing additional cameras and sensors to be added in new venues or more areas where Edge computing might be required.
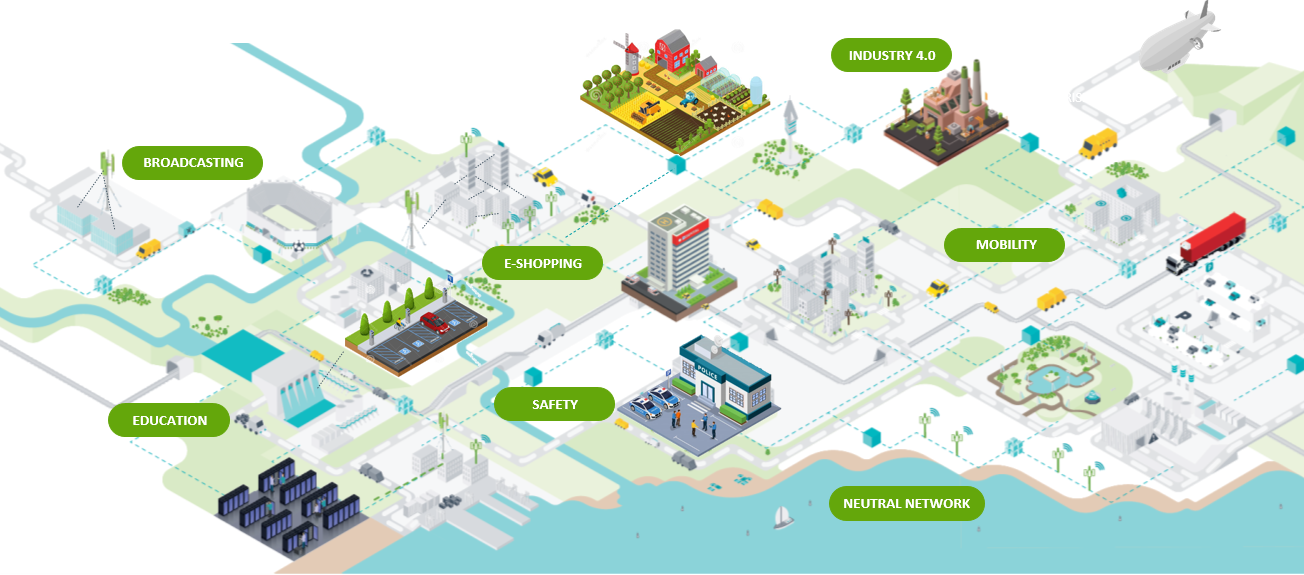
Many different use cases can come up when we talk about smart cities, such as:
- Manage Traffic: Video analysis of traffic flows can feed into signal timing to optimize travel time for citizens, limit congestion, and reduce pollution.
- Save Energy: Combining environmental and personnel usage data with building control systems can help reduce energy consumption.
- Optimize Parking: Real-time information of open parking spots can be provided to command center, city visitors, and control ingress - egress in emergencies.
- Manage Lighting: Motion and infra-red sensors can monitor movement and presence, reducing energy, and maintaining public safety
- Reduce Water Pollution: Monitoring pollution levels at points of interest can detect water quality issues and contaminants early to reduce impact on the environment and water supply.
- Provide Campus Navigation: Indoor navigation to find places of interest, optimal routes, and emergency exits.
- Optimize Fleets: Connected vehicle tracking allows for better management of large fleets reducing costs, optimizing asset usage, and providing prescriptive service as problems arise, and preventing loss.
- Air Quality Control: By analyzing air pollution data, traffic and industry can be adjusted to reduce harmful levels in highly polluted areas and citizens can be notified to limit outside activity.
- Detect Gas and Water Leaks: Smart meters with embedded sensors can measure consumption and detect leaks.
- Detect Crime: Video feed can be analyzed in real time for crime and help authorities find criminals.
- Smart Energy Management: Tracking and management of energy peak-time consumption in residential and industrial facilities can ensure grid reliability.
- Public Transport: Live video streams, live bus tracking, and enabling Wi-Fi services enhances citizen and visitor experience, while using public transport.
Barcelona: A flag ship smart city
Barcelona is a leading European city in implementing data-driven, smart city technologies to improve its services. As part of this initiative, in 2015 Barcelona started a process of network transformation and different pilots across the city.
The City of Barcelona has set an ambitious plan for digital transformation that will place the city in the vanguard of efficiency, transparency, and social innovation. This plan includes strategic projects to counter social problems detected as government priorities.
In July 2019, Red.es, a public entity under the Spanish ministry of economy awarded the development of a 5G pilot in the Barcelona metropolitan area to a consortium of companies to test and develop innovative solutions based on this new technology in sectors that include education, industry, commerce, tourism, transport, and safety and emergency management.

Implementation challenges
Industries such as transportation, government, healthcare, gaming, education, manufacturing, and hospitality are adding different applications to be deployed across edge solutions capabilities but are struggling with how to implement the solutions. How to handle the massive size of projects, brownfield integration,(integrating existing systems with the rest of the world, which has to be done with more care than building a system from scratch), and security are all top of mind. Current systems often cannot handle future growth which leaves IT owners choosing between overspending today or delaying upgrades. Scalability is key. They need a partner they can count on to help them scope, implement, and manage such a solution.
Lenovo is part of a consortium of 8 companies, working very closely with different institutions, partners and customers starting to deliver an enterprise-class smart city infrastructure that is easy to manage, simple to deploy, and scales as needs grow.
Barcelona Smart City architecture
Lenovo´s role in this project is to supply the smart infrastructure which will support the deployment of a private 5G stand alone network running on different nodes of the ThinkEdge SE450 as well as the software solution Lenovo Open Cloud Automation (LOC-A).
Lenovo Open Cloud Automation (LOC-A) is a software that provides end-to-end automation, simplifies and streamlines manual error-prone processes. LOC-A provides an automation platform that orchestrates the entire chain of events/tools from hardware configuration to operating systems installation to cloud and networking layer deployment. So servers simply need to be turned ON and LOC-A handles everything else to bring the infrastructure into service. Lenovo is contributing to the project with edge servers and software capabilities to deploy and manage these highly distributed compute fabrics. Lenovo’s datacenter servers, combined with ruggedized, secure edge servers provide compute capabilities directly in the streets of Barcelona where the data is created and consumed.
Nearby One, a product from Nearby Computing provides the overall edge orchestration capabilities. Once the infrastructure is provisioned by LOC-A, Nearby One springs into action and deploys the edge applications based on pre-defined business Service Level Agreements (SLA). The lifecycle management of those applications, along with the dynamic monitoring of the applications performances assure an optimal performance.
Barcelona´s use cases
It is a collaboration that will allow us to lay the foundations to accelerate the digital transformation of the city of Barcelona. The collaboration allows us to lay the foundation to accelerate the digital transformation of the city of Barcelona. With the cooperation of the public and private sectors, at different levels and the acceleration of an ecosystem of technology companies we will provide excellent value to citizens, companies and public entities.
It involves deploying and testing innovative solutions in sectors as relevant as education, industry, commerce, tourism, transport, etc. that could lead in the future to generalize these services for all citizens through the installation of thousands of servers taking advantage of high-speed and low latency 5G networks.
Figure 1. High-level view of use cases to be implemented
Where can I find the edge nodes in Barcelona?
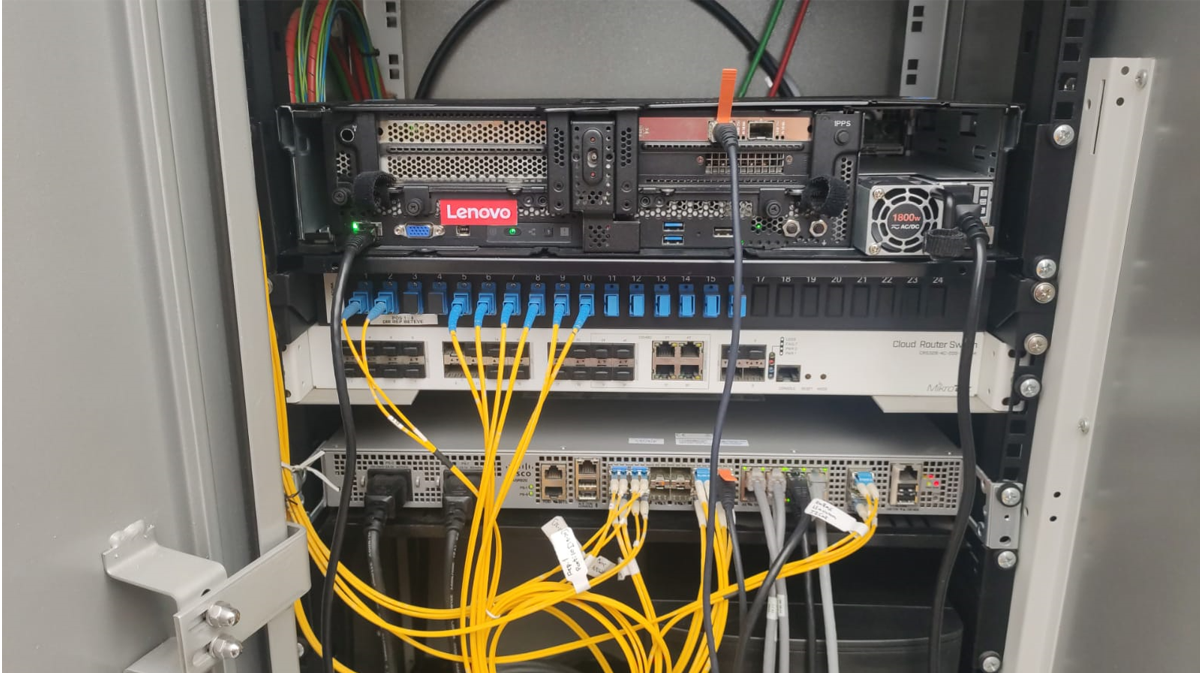
When you drive or walk through a city, you will see many street cabinets.
The street cabinet is defined as a communications provider site of existing street cabinets owned and controlled by the communications provider (or local authority), located in the street and used to host communications SP equipment.
In a city like Barcelona, there are more than 3,000 street cabinets, which means an incredible opportunity to transform any city or town. Below you can see how a real street cabinet looks like.
It is essential to mention that the different use cases currently being implemented in Barcelona, are only a few and many others could apply to your city, you can find more use cases in this article´s What makes a city "smart" section.
Learn more about the SE450 by viewing the ThinkEdge SE450 datasheet.
Related product families
Product families related to this document are the following:
Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
ThinkEdge®
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.