Author
Published
25 Aug 2020Form Number
LP1349PDF size
6 pages, 193 KBAbstract
With the August 2020 UEFI release, Lenovo ThinkSystem servers with second-generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors offer a new UEFI setting for Intel Optane Persistent Memory 100 Series (PMem) called the “Balanced Profile”. The purpose of this new setting is to optimize both bandwidth and latency performance for system memory (DRAM and PMem) in two-level (2LM) memory mode. The Balanced Profile is in addition to the existing Bandwidth Optimized and Latency Optimized profiles.
Introduction
The Intel Optane Persistent Memory (PMem or DCPMM) provides higher memory capacity support than traditional DRAM which can benefit various applications with massive memory requirements such as virtualization, high-performance computing (HPC), big-data analytics, in-memory databases, Video on Demand (VoD) and SAP HANA.
PMem can be configured in Memory Mode, App Direct Mode, and Mixed Mode (combine Memory and App Direct Mode) to adapt to different user scenarios. Focusing on Memory Mode, this paper elaborates on the low-level access mechanism between DRAM and PMem to explain the difference between the Balanced, Bandwidth Optimized and Latency Optimized profiles for PMem.
Note: The Balanced Profile setting is currently only available on systems with Intel Optane Persistent Memory 100 Series and second-generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors.
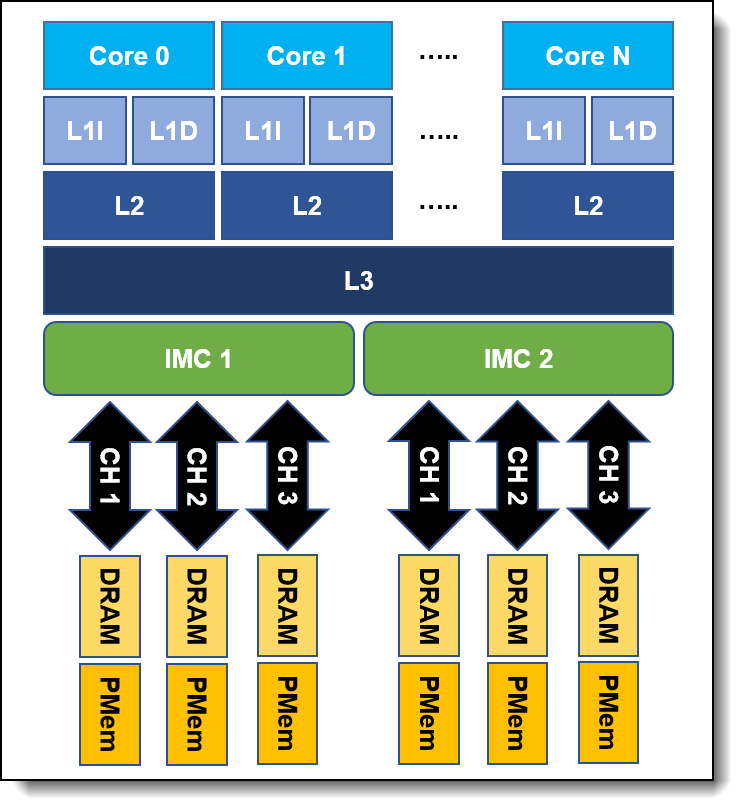
Two-Level Memory Architecture
Managed by the memory controller inside Intel Xeon Scalable Processor, PMem adopts a Two-Level Memory (2LM) Architecture in Memory Mode as shown in the following figure. Different from a legacy memory hierarchy, the DRAM under the 2LM topology is treated as an L4 cache to store frequently used data, alongside the PMem working as system memory to provide a larger memory capacity compared to DRAM alone for memory hungry applications.
In 2LM mode, DRAM acts as the next level cache (L4), and PMem acts as system main memory. When data is found in DRAM, it is an L4 hit and access latency is the same as the latency to DRAM. However, when data is not found at DRAM, it is an L4 miss, and memory controller has to access data from PMem. This access from PMem, when it happens, incurs higher memory latency.
UEFI Preset Modes for PMem
Based on the 2LM topology, the memory controller can only request data from either DRAM or the PMem at a time, such that the dispatch ratio between DRAM and PMem would be a crucial factor of the system performance. Fine tuning numerous thresholds along with dispatch ratio of memory controller and related parameters in the BIOS, Lenovo introduces a new Balanced Profile for PMem memory mode. Based on internal test results, the performance of both memory bandwidth and latency improved significantly when the Balanced Profile was applied.
With the introduction of Balanced Profile, Lenovo now offer three different PMem preset modes in the BIOS to adapt various kind of workloads, as listed in the following table.
| Profile | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Balanced (default) | Optimize PMem Profile for Memory Mode |
| BW Optimized | Optimize Bandwidth on both L4 cache and PMem |
| Latency | Optimize L4 cache Latency in the presence of PMem Bandwidth |
While the Balanced Profile is recommended as the default preset mode for PMem memory mode, users can change preset mode as needed by clicking through the following menu selections in System Setup in UEFI: System Settings > Socket Configuration > Memory Configuration > NGN Configuration > NVM Performance Setting. Then select from these choices as shown in the following figure:
- BW Optimized
- Latency Optimized
- Balanced Profile
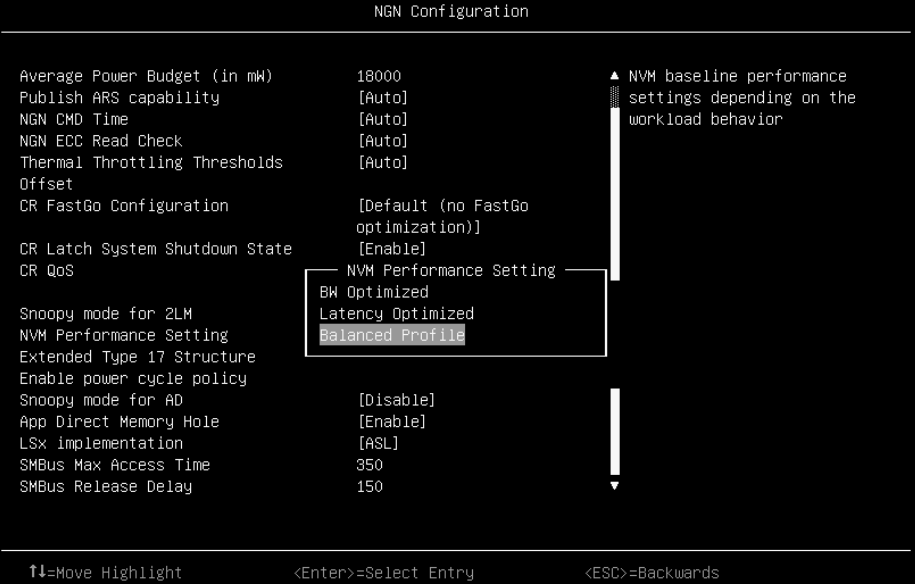
Figure 2. PMem performance mode settings (click the image for a larger version)
OneCLI V2.5.0 or later supports Intel PMem and can also be used to setup the PMem performance mode by using the OneCLI command as shown below:
./OneCli config set IntelOptaneDCPMM.DCPMMPerformanceSetting "Latency Optimized"
./OneCli config set IntelOptaneDCPMM.DCPMMPerformanceSetting "BW Optimized"
./OneCli config set IntelOptaneDCPMM.DCPMMPerformanceSetting "Balanced Profile"
Example out of the OneCLI config set command is shown in the following figure.
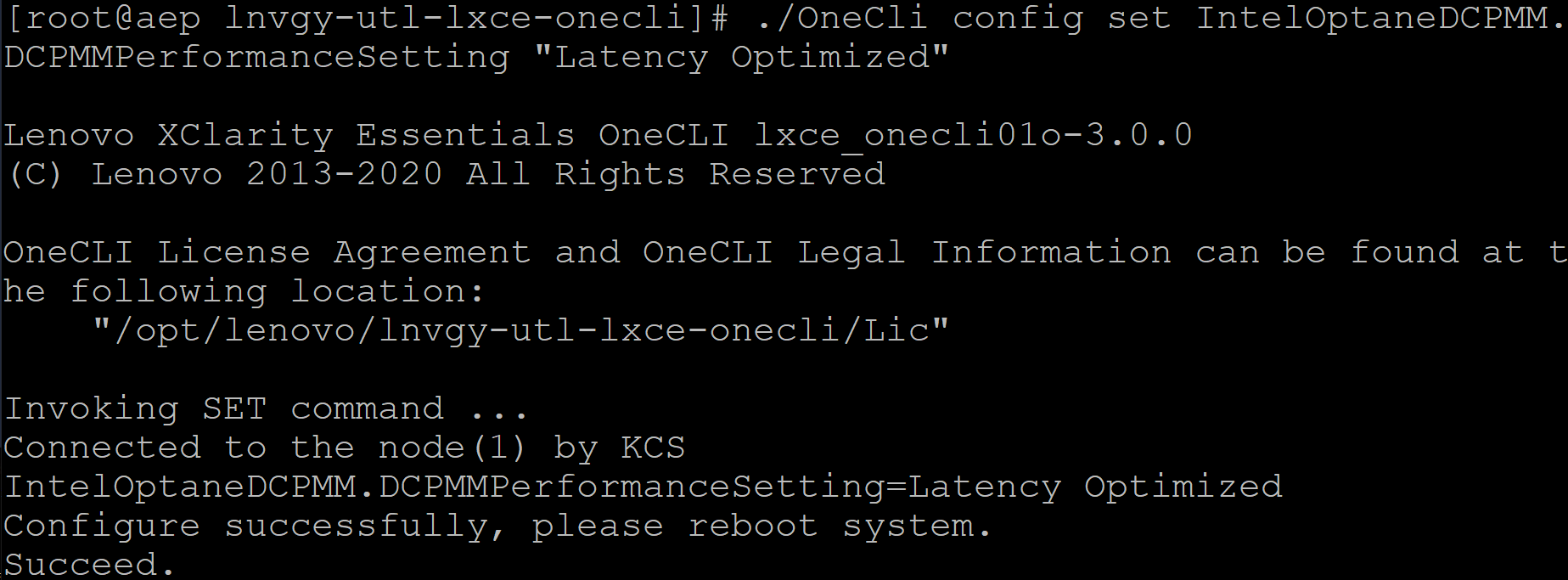
Figure 3. OneCLI config set command (click the image for a larger version)
About the author
Jimmy Cheng is a performance engineer in the Lenovo Infrastructure Solutions Group (ISG) Performance Laboratory in Taipei, Taiwan. Jimmy joined Lenovo in December 2016. Prior to this, he worked on IBM POWER system assurance and validation, system integration, automation development as well as network performance. Jimmy holds a master’s degree in Electronic and Computer Engineering from National Taiwan University of Science and Technology in Taiwan, and a bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science and Engineering from Yuan-Ze University, Taiwan.
Thanks to the following people for their contributions to this project:
- Joe Jakubowski, Principal Engineer and Performance Architect in the Lenovo ISG Performance Laboratory in Morrisville, NC
- Nathan Pham, Sr. Performance Engineer and Architect in the Lenovo ISG Performance Laboratory in Morrisville, NC
- Arunkumar Krishnamoorthy, Server Performance Development Engineer in the Lenovo ISG Performance Laboratory in Morrisville, NC
- David Watts, Lenovo Press
Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
ThinkSystem®
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Intel®, Intel Optane™, and Xeon® are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.