Abstract
In today’s environment as data center space is constrained and IT budgets get smaller, clients are looking for ways to increase utilization of their hardware. Virtualization offers the perfect platform by allowing clients to implement multiple virtual machines per server. To meet client requirements, BladeCenter offers the right balance of compute and I/O by offering high-performance servers, such as HS23 and next-generation 10Gb networking from System x Networking.
Change History
Changes in the November 4 update:
- Updated product descriptions
- Updated Transceivers and cables
- Updated Features and specifications
- Updated Typical configurations
- Updated Related publications and links
- Removed withdrawn options
- Updated formatting
Introduction
The BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module for offers the most bandwidth of any blade switch and represents the perfect migration platform for clients who are still at 1 Gb outside the chassis by seamlessly integrating in the existing 1 Gb infrastructure. This is the first 10 Gb switch for BladeCenter that is convergence ready (that is, able to transmit Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) to a Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) capable top-of-rack switch).
In addition, this switch is a key part of the Virtual Fabric offering, which allows clients to form up to eight virtual network interface controllers (vNICs) from one physical adapter (14 vNICs with an adapter plus the onboard 10 GbE controller with the BladeCenter HS23) and to manage them in virtual groups. This switch can be managed via a command-line interface (CLI) or a graphical interface of the switch, providing all the benefits of I/O Virtualization at 10 Gb speeds. Figure 1 shows the switch module.

Figure 1. BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module
Did you know?
As virtualization has become a prevalent standard in the data center, more people have been looking for ways to virtualize I/O to reduce cost and complexity while also maximizing I/O resources. Virtual Fabric for BladeCenter provides fast, flexible, easy, and reliable I/O using the Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module and the Emulex Virtual Fabric Adapter, which provides the abilities to carve up an adapter into eight virtual NICs, dynamically allocate bandwidth, manage virtual groups, and so on. With the BladeCenter HS23, a total of 14 vNICs can be configured using the Emulex VFA II for HS23 plus the onboard Emulex controller.
The switch is designed to support a number of different types of configurations from the blade: 1 Gb, 10 Gb, virtual NIC, Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE/FCoE), and iSCSI. If you have a chassis with multiple servers, some operating at 1 Gb, some at 10 Gb, and some transmitting converged packets, this single switch can handle all these workloads and can connect to a 1 Gb infrastructure or a 10 Gb infrastructure, or both.
Ordering information
Table 1 shows the part numbers and feature codes for ordering the Virtual Fabric 10 Gb Switch Module.
| Description | Part number | Feature code |
| BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module | 46C7191 | 1639 |
The module part number, 46C7191, include the following items:
- One BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module
- 3-meter mini-USB-to-DB9 serial console cable
- One filler module
- BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module Installation Guide
- BladeCenter user license agreement
- Important Notices document
- Documentation CD-ROM
Note: Transceivers and cables are not included with the switch module. (See Table 2 for options.)
Transceivers and cables
With the flexibility of the BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module, clients can use the technologies that are required for the following environments:
- For 1 GbE links, clients can use RJ-45 SFP transceivers with UTP cables up to 100 meters. Clients that need longer distances can use a 1000BASE-SX transceiver, which can drive distances up to 220 meters by using 62.5 µ multi-mode fiber and up to 550 meters with 50 µ multi-mode fiber, or the 1000BASE-LX transceivers that support distances up to 10 kilometers by using single-mode fiber (1310 nm).
- For 10 GbE (on external SFP+ ports), clients can use SFP+ direct-attached copper (DAC) cables for in-rack cabling and distances up to 7 meters. These DAC cables have SFP+ connectors on each end, and they do not need separate transceivers. For longer distances, the 10GBASE-SR transceiver can support distances up to 300 meters over OM3 multimode fiber or up to 400 meters over OM4 multimode fiber. The 10GBASE-LR transceivers can support distances up to 10 kilometers on single mode fiber. For extended distances, the 10GBASE-ER transceivers can support distances up to 40 kilometers on single mode fiber.
The supported cables and transceivers are listed in Table 2.
| Description | Part number | Feature code | Maximum quantity supported |
| SFP transceivers - 1 GbE | |||
| Lenovo 1000BASE-T SFP Transceiver (RJ-45) (no 10/100 Mbps support) | 00FE333 | A5DL | 10 |
| Lenovo 1000BASE-SX SFP Transceiver | 81Y1622 | 3269 | 10 |
| Lenovo 1000BASE-LX SFP Transceiver | 90Y9424 | A1PN | 10 |
| SFP+ transceivers - 10 GbE | |||
| Lenovo 10GBASE-SR SFP+ Transceiver | 46C3447 | 5053 | 10 |
| Lenovo 10GBASE-LR SFP+ Transceiver | 90Y9412 | A1PM | 10 |
| Lenovo 10GBASE-ER SFP+ Transceiver | 90Y9415 | A1PP | 10 |
| Optical cables for 1 GbE SX SFP and 10 GbE SR SFP+ transceivers | |||
| Lenovo 0.5m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN499 | ASR5 | 10 |
| Lenovo 1m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN502 | ASR6 | 10 |
| Lenovo 3m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN505 | ASR7 | 10 |
| Lenovo 5m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN508 | ASR8 | 10 |
| Lenovo 10m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN511 | ASR9 | 10 |
| Lenovo 15m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN514 | ASRA | 10 |
| Lenovo 25m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN517 | ASRB | 10 |
| Lenovo 30m LC-LC OM3 MMF Cable | 00MN520 | ASRC | 10 |
| Passive SFP+ direct-attach cables - 10 GbE | |||
| Lenovo 0.5m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 00D6288 | A3RG | 10 |
| Lenovo 1m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 90Y9427 | A1PH | 10 |
| Lenovo 1.5m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 00AY764 | A51N | 10 |
| Lenovo 2m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 00AY765 | A51P | 10 |
| Lenovo 3m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 90Y9430 | A1PJ | 10 |
| Lenovo 5m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 90Y9433 | A1PK | 10 |
| Lenovo 7m Passive SFP+ DAC Cable | 00D6151 | A3RH | 10 |
| Active SFP+ direct-attach cables - 10 GbE | |||
| 1m 10GE Twinax Act Copper SFP+ | 81Y8295 | A18M | 10 |
| 3m 10GE Twinax Act Copper SFP+ | 81Y8296 | A18N | 10 |
| 5m 10GE Twinax Act Copper SFP+ | 81Y8297 | A18P | 10 |
Benefits
The Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module offers the following benefits:
- Integration and consolidation: This switch consolidates full Layer 2-3 LAN switching and routing capabilities into a single BladeCenter chassis. This helps flatten the data center infrastructure and reduces the number of discrete devices, management consoles, and equipment that administrators must deal with, helping lower costs and simplifying deployment.
- Cost: The switch is priced extremely competitively compared with external switches, especially when you factor in that no cables are required between the blade and the switch. In addition, the ability to use direct-attach cables with the switch can help clients save even more compared with the more expensive CX4, XFP, or X2 transceivers.
- Performance: With support for ten 10 Gb uplinks, clients can exploit not only up to 200 Gbps of bi-directional uplink bandwidth, but also an extremely low oversubscription (14 to 10), which can support even the most performance-intensive environments (up to 7.2 Gbps per blade server port). Clients wanting extreme performance can use up to four switches and the quad port 10 Gb adapter and get up to 1.92 Tbps of data per BladeCenter H chassis.
- Lower power consumption: Using only 75 W per switch delivers extreme performance per watt, which is second to none with its support for up to 6.4 Gbps per watt of power.
- Layer 3 functionality: The switch module includes Layer 3 functionality, which provides security and performance benefits as inter-VLAN traffic stays within the chassis. This switch also provides the full range of Layer 3 protocols from static routes for technologies such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for enterprise customers.
- Interoperability: Lenovo switches interoperate seamlessly with other vendors' upstream switches.
- Management: Lenovo provides a choice of interfaces that IT staff can use for management which includes an industry-based CLI (Cisco-like) for those familiar with IOS, and a full-function Web-based GUI for the latest in simplicity.
- Fault tolerance: These switches learn alternate routes automatically and perform faster convergence in the unlikely case of a link, switch, or power failure. The switch uses proven technologies like L2 trunk failover, advanced VLAN-based failover, VRRP, IGMP V3 snooping, and OSPF.
- Converged fabric: The switch is designed to support CEE and connectivity to FCoE modules, making the Lenovo solution fully FCoE capable. CEE will help enable clients to combine storage, messaging traffic, VoIP, video, and other data on a common data center Ethernet infrastructure. FCoE will help enable highly efficient block storage over Ethernet for consolidating server network connectivity. As a result, clients can deploy a single server interface for multiple data types, which can simplify both deployment and management of server network connectivity, while maintaining the high availability and robustness required for storage transactions.
With the combination of the switch and the QLogic Virtual Fabric Extension Module for BladeCenter, Lenovo is able to deliver a full integrated FCoE blade solution that appeals to those clients who require separate LAN and SAN traffic outside the chassis due to internal politics or for those wanting to implement FCoE but are extremely cost-sensitive. For information about the QLogic Virtual Fabric Extension Module, see:
http://lenovopress.com/tips0717
In addition, the switch also supports CEE/DCB which allows clients to forward the FCoE traffic upstream to a Top-of-Rack Gateway device that will split out the LAN traffic (Ethernet) and the SAN (Fiber Channel) traffic. For the latest FCoE gateway devices that are supported visit:
http://lenovopress.com/bcig
- Virtual Fabric for BladeCenter: This feature enables clients to implement and manage the Virtual Fabric solution via a graphical interface or CLI. It is through this that administrators can perform tasks such as activating a Virtual Fabric, selecting the number of virtual NICs (vNICs), dynamically allocating bandwidth, creating virtual groups to simplify management, and setting up the failover and isolation capabilities to the vNICs for better availability and security. This switch also offers the benefit of Lenovo’s next-generation vNIC - Unified Fabric Port (UFP). UFP is an advanced, cost-effective solution that provides a flexible way for clients to allocate, reallocate, and adjust bandwidth to meet their ever-changing data center requirements.
- VMready: VMready is a unique solution that enables the network to be virtual machine-aware. The network can be configured and managed for virtual ports (v-ports) rather than just for physical ports. With VMready, as VMs migrate across physical hosts, so do their network attributes. Virtual machines can be added, moved, and removed while retaining the same ACLs, QoS, and VLAN attributes. VMready allows for a define-once-use-many configuration that evolves as the server and network topologies evolve. VMready works with all virtualization products, including VMware, Hyper-V, Xen, and KVM, without modification of virtual machine hypervisors or guest operating systems.
Features and specifications
The BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module includes the following features and functions (software features are based on the Networking OS version 7.8):
- Form-factor
- Single-wide high-speed switch module
- Internal ports
- 14 internal auto-negotiating ports: 1 Gb or 10 Gb to the server blades
- Two internal full-duplex 100 Mbps ports connected to the management module
-
External ports
- Up to ten 10 Gb SFP+ ports (also designed to support 1 Gb SFP if required, flexibility of mixing 1 Gb/10 Gb)
- One 10/100/1000 Mb copper RJ-45 used for management
- An RS-232 mini-USB connector for serial port that provides an additional means to install software and configure the switch module
- Scalability and performance
- Stacking support up to 8 switches
- Autosensing 1 Gb/10 Gb internal and external Ethernet ports for bandwidth optimization
- Non-blocking architecture with wire-speed forwarding of traffic and full line rate performance of 480 Gbps full duplex
- Media access control (MAC) address learning: automatic update, supports up to 32 Kb MAC addresses
- Up to 128 IP interfaces per switch
- Static, EtherChannel, and LACP (IEEE 802.3ad) link aggregation, up to 100 Gb of total bandwidth per switch, up to 18 trunk groups, and up to eight ports per group
- Support for jumbo frames (up to 9,216 bytes)
- Broadcast/multicast storm control
- IGMP snooping for limit flooding of IP multicast traffic (IGMP V1, V2, and V3)
- Configurable traffic distribution schemes over trunk links based on source/destination IP addresses, MAC addresses, or both
- Fast port forwarding and fast uplink convergence for rapid STP convergence
- Availability and redundancy
- VRRP for Layer 3 router redundancy
- IEEE 802.1D STP for providing Layer 2 redundancy with PVRST+
- IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) for topology optimization, up to 128 STP instances supported by single switch
- IEEE 802.1w Rapid STP (RSTP), providing rapid STP convergence for critical delay-sensitive, traffic-like voice or video
- Layer 2 Trunk Failover to support active/standby configurations of network adapter teaming on blades
- Interchassis redundancy (Layer 2 and Layer 3)
- VLAN support
- Up to 1024 VLANs supported per switch; VLAN numbers ranging from 1 to 4095 (4095 is used for the management module’s connection only.)
- 802.1Q VLAN tagging support on all ports
- Ingress VLAN tagging support to tunnel packets through a public domain without altering the original 802.1Q
- Port-based and protocol-based VLANs
- Private VLANs
- Security
- VLAN-based, MAC-based, and IP-based access control lists (ACLs)
- 802.1X port-based authentication
- Multiple user IDs and passwords
- User access control
- Radius, TACACS+, LDAP authentication and authorization
- NIST 800-131A Encryption
- Quality of service (QoS)
- Support for IEEE 802.1p, IP ToS/DSCP, and ACL-based (MAC/IP source and destination addresses, VLANs) traffic classification and processing
- Traffic shaping and re-marking based on defined policies
- Up to eight weighted round robin (WRR) priority queues per port for processing qualified traffic
- IPv4/IPv6 ACL metering
- IP v4 Layer 3 functions
- Host management
- IP forwarding
- IP filtering with ACLs; up to 256 ACLs supported
- VRRP for router redundancy
- Support for up to 128 static routes
- Routing protocol support (RIP v1, RIP v2, OSPF v2, and BGP-4); up to 1,024 entries in a routing table
- Support for DHCP Relay
- Support for IGMP snooping and IGMP relay
- IPv6 Layer 3 functions
- IPv6 host management (except default switch management IP address)
- IPv6 forwarding
- Up to 128 static routes
- Support for OSPF v3 routing protocol
- IPv6 filtering with ACLs; up to 128 ACLs supported
- Virtualization
- Virtual NICs (vNICs): Ethernet, iSCSI, or FCoE traffic is supported on vNICs
- Unified fabric port (UFP):
- Ethernet, iSCSI, or FCoE traffic is supported on UFPs
- Supports up to 256 VLAN for the virtual ports
- Integration with L2 failover
- Virtual link aggregation groups (vLAGs)
- 802.1Qbg Edge Virtual Bridging (EVB) is an emerging IEEE standard for allowing networks to become virtual machine (VM)-aware:
- Virtual Ethernet Bridging (VEB) and Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator (VEPA) are mechanisms for switching between VMs on the same hypervisor.
- Edge Control Protocol (ECP) is a transport protocol that operates between two peers over an IEEE 802 LAN that provides reliable, in-order delivery of upper layer protocol data units.
- Virtual Station Interface (VSI) Discovery and Configuration Protocol (VDP) allows centralized configuration of network policies that persist with the VM, independent of its location.
- EVB Type-Length-Value (TLV) is used to discover and configure VEPA, ECP and VDP.
- VMready
- Up to 2,048 virtual entities (VEs)
- Automatic VE discovery
- Up to 1,024 local or distributed VM groups for VEs
- NMotion® feature for automatic network configuration migration
- Converged Enhanced Ethernet
- Priority-Based Flow Control (PFC) (IEEE 802.1Qbb) extends 802.3x standard flow control to allow the switch to pause traffic that is based on the 802.1p priority value in each packet’s VLAN tag.
- Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) (IEEE 802.1Qaz) provides a method for allocating link bandwidth that is based on the 802.1p priority value in each packet’s VLAN tag.
- Data Center Bridging Capability Exchange Protocol (DCBX) (IEEE 802.1AB) allows neighboring network devices to exchange information about their capabilities.
- Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)
- FC-BB5 FCoE specification compliant
- FCoE transit switch operations
- FCoE Initialization Protocol (FIP) support for automatic ACL configuration
- FCoE Link Aggregation Group (LAG) support
- Supports up to 2,048 FCoE connections
- Supports the QLogic Virtual Fabric Extension Module for BladeCenter, which provides FCoE gateway functionality inside the BladeCenter chassis.
- Stacking
- Up to eight switches in a stack; single IP management
- FCoE support
- FCoE LAG on external ports
- 802.1Qbg support
- vNIC and UFP support
- Manageability
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP, V1, V2, and V3)
- HTTP/HTTPS browser GUI
- Industry-standard CLI or menu-driven CLI
- Telnet interface for CLI
- SSH V2
- Serial interface for CLI
- Scriptable CLI
- Firmware image update (TFTP and FTP)
- Network Time Protocol (NTP) for switch clock synchronization
- Switch Center support
- Monitoring
- Switch LEDs for external port status and switch module status indication
- Port mirroring for analyzing network traffic passing through switch
- Change tracking and remote logging with syslog feature
- Support for sFLOW agent for monitoring traffic in data networks (separate sFLOW analyzer required elsewhere)
- POST diagnostics
- Special functions
- Serial over LAN (SOL)
The following features are not supported with IPv6:
- Default switch management IP address
- SNMP trap host destination IP address
- Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) and DHCP
- RADIUS, TACACS+ and LDAP
- QoS metering and re-marking ACLs for out-profile traffic
- VMware Virtual Center (vCenter) for VMready
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
- sFLOW
The following features are not supported with Stacking (for more information about limitations, see the Networking OS Application Guide):
- IGMP Relay and IGMPv3
- IPv6
- Routing protocols (RIP, OSPF, BGP)
- sFLOW
- Static MAC addresses
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
The switch supports the following standards:
- IEEE 802.1AB Data Center Bridging Capability Exchange Protocol (DCBX)
- IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- IEEE 802.1p Class of Service (CoS) prioritization
- IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP)
- IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN (frame tagging on all ports when VLANs are enabled)
- IEEE 802.1Qbg Edge Virtual Bridging
- IEEE 802.1Qbb Priority-Based Flow Control (PFC)
- IEEE 802.1Qaz Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS)
- IEEE 802.1x port-based authentication
- IEEE 802.1w Rapid STP (RSTP)
- IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T copper twisted pair Gigabit Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol
- IEEE 802.3ae 10GBASE-KR backplane 10 Gb Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3ae 10GBASE-SR short range fiber optics 10 Gb Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3ae 10GBASE-LR long range fiber optics 10 Gb Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3ae 10GBASE-ER extended range fiber optics 10 Gb Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3x Full-duplex Flow Control
- IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-SX short range fiber optics Gigabit Ethernet
- IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-LX long range fiber optics Gigabit Ethernet
- SFF-8431 10GSFP+Cu SFP+ Direct Attach Cable
Chassis and expansion cards
The Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch is supported in the BladeCenter H and HT chassis, as shown in Table 3.
| BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module | 46C7191 | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N |
Table 4 lists the the expansion cards that are compatible with the BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch.
| Description | Part number | Feature code |
| Gigabit Ethernet | ||
| 2/4 Port Ethernet Expansion Card (CFFh) | 44W4479 | 5476 |
| 10 Gigabit Ethernet | ||
| 10Gb Interposer Card for HS23 (uses HS23 Integrated Virtual Fabric LOM) | 94Y8550 | A244 |
| Broadcom 10Gb Gen 2 4-port Ethernet Expansion Card | 46M6164 | 0098 |
| Broadcom 10Gb Gen 2 2-port Ethernet Expansion Card | 46M6168 | 0099 |
| Broadcom 2-port 10Gb Virtual Fabric Adapter | 81Y3133 | A1QR |
| Brocade 2-port 10GbE Converged Network Adapter | 81Y1650 | 5437 |
| Emulex 10GbE Virtual Fabric Adapter | 49Y4235 | 5755 |
| Emulex 10GbE Virtual Fabric Adapter Advanced | 49Y4275 | 2435 |
| Emulex Virtual Fabric Adapter II (CFFh) | 90Y3550 | A1XG |
| Emulex Virtual Fabric Adapter Advanced II (CFFh) | 90Y3566 | AIXH |
| Emulex 10GbE VFA II for BladeCenter HS23 | 81Y3120 | A287 |
| Emulex 10GbE VFA Advanced II for BladeCenter HS23 | 90Y9332 | A2ZN |
| Mellanox 10 Gb Ethernet Expansion Card (CFFh) | 90Y3570 | A1NW |
| QLogic 2-port 10Gb Converged Network Adapter (CFFh) | 00Y3280** | A3JB |
| QLogic 10Gb Virtual Fabric Adapter | 00Y3332 | A4AC |
| QLogic 10Gb Virtual Fabric CNA | 00Y5618 | A4AD |
* Replaces 44X1940.
** Replaces 42C1830.
The five BladeCenter chassis have the following bays:
- BladeCenter S, E, and T have four standard I/O bays (1, 2, 3, and 4)
- BladeCenter H has six standard I/O bays (1, 2, 3, 4), two bridge bays (5 and 6) and four high-speed bays (7, 8, 9, and 10)
- BladeCenter HT has four standard I/O bays (1, 2, 3, 4) and four high-speed bays (7, 8, 9, and 10).
The BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module fits in one of the high-speed I/O bay (bays 7-10). For each supported adapter, the Table 5 lists which specific chassis I/O bays are supported.
| Description | Part number | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10Gb Interposer Card for HS23 | 94Y8550 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| 2/4 Port Ethernet Expansion Card (CFFh) | 44W4479 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Broadcom 10Gb Gen 2 2-port Ethernet Exp. Card | 46M6168 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Broadcom 10Gb Gen 2 4-port Ethernet Exp. Card | 46M6164 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Broadcom 2-port 10Gb Virtual Fabric Adapter | 81Y3133 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Brocade 2-port 10GbE CNA | 81Y1650 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Emulex 10GbE Virtual Fabric Adapter | 49Y4235 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Emulex 10GbE Virtual Fabric Adapter Advanced | 49Y4275 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Emulex 10GbE Virtual Fabric Adapter II | 90Y3550 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Emulex 10GbE Virtual Fabric Adapter II Advanced | 90Y3566 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Emulex 10GbE VFA II for HS23 | 81Y3120 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Emulex 10GbE VFA Advanced II for HS23 | 90Y9332 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Mellanox 2-port 10Gb Ethernet Expansion Card | 90Y3570 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| QLogic 2-port 10Gb Converged Network Adapter | 42C1830 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| QLogic 10Gb Virtual Fabric Adapter | 00Y3332 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| QLogic 10Gb Virtual Fabric CNA | 00Y5618 | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
* These ports are available by routing the onboard Emulex BE3 controller of the HS23 blade server through the VFA card.
Connectors and LEDs
Figure 2 shows the front panel of the BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module.
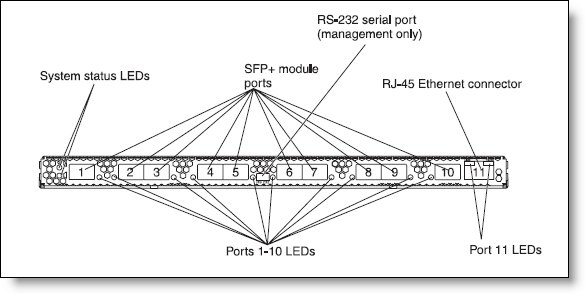
Figure 2. Front panel of the BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module
The front panel contains the following components:
- LEDs display the status of the switch module and the network:
- OK: indicates that the switch module has passed the power-on self-test (POST) with no critical faults and is operational
- Switch-module error: indicates that the switch module has failed the POST or detected an operational fault
- One USB RS-232 console port provides an additional means to install software and configure the switch module. This USB-style connector enables the connection of a special serial cable that is supplied with the switch module.
- Ten SFP+ port connectors to attach SFP+ modules.
- One RJ-45 Ethernet port connector for management.
- Each external SFP+ port on the switch module contains a link/activity LED, and an RJ-45 port contains Ethernet link OK and Ethernet Tx/Rx activity LEDs.
Network cabling requirements
The network cables that can be used with the switch are shown in Table 6.
Table 6. Virtual Fabric 10 GbE switch network cabling requirements
| Transceiver | Standard | Cable | Connector |
| 10 Gb Ethernet | |||
| 10GBASE-SR SFP+ Transceiver (46C3447) | 10GBASE-SR | Up to 30 m with fiber optic cables supplied by Lenovo (see Table 2); 850 nm OM3 multimode fiber cable (50 µ or 62.5 µ) up to 300 m or up to 400 m with OM4 multimode fiber | LC |
| 10GBASE-LR SFP+ Transceiver (90Y9412) | 10GBASE-LR | 1310 nm single-mode fiber cable up to 10 km | LC |
| 10GBASE-ER SFP+ Transceiver (90Y9415) | 10GBASE-ER | 1310 nm single-mode fiber cable up to 40 km | LC |
| Direct attach cable | 10GSFP+Cu | SFP+ DAC cables up to 7 m (see Table 2) | SFP+ |
| 1 Gb Ethernet | |||
| 1000BASE-T SFP Transceiver (00FE333) | 1000BASE-T | UTP Category 5, 5E, and 6 up to 100 meters | RJ-45 |
| 1000BASE-SX SFP Transceiver (81Y1622) | 1000BASE-SX | Up to 30 m with fiber optic cables supplied by Lenovo (see Table 2); 850 nm multimode fiber cable up to 550 m (50 µ) or up to 220 m (62.5 µ) | LC |
| 1000BASE-LX SFP Transceiver (90Y9424) | 1000BASE-LX | 1310 nm single-mode fiber cable up to 10 km | LC |
| Management ports | |||
| External 1 GbE management port | 1000BASE-T | UTP Category 5, 5E, and 6 up to 100 meters | RJ-45 |
| External RS-232 management port | RS-232 | DB-9-to-mini-USB console cable (comes with the switch) | Mini-USB |
Warranty
The switch carries a 1-year, customer-replaceable unit (CRU) limited warranty. When installed in a chassis, these I/O modules assume your system’s base warranty and any warranty service upgrade. The software license will match the warranty and allows for the download of new software releases.
Typical configurations
The BladeCenter Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module can be used in various configurations. The following usage scenarios are described:
- 10 Gb Ethernet Virtual Fabric
- Converged iSCSI or FCoE network
10 Gb Ethernet Virtual Fabric
The Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch Module UFP solution is based on a BladeCenter chassis with a 10 Gb Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) infrastructure and 10 Gb Virtual Fabric Adapters (VFAs) installed in each blade server.
In UFP mode, the Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch is vPort-aware; that is, the configuration of vPorts is performed on a switch, then it propagates vPorts parameters to VFA. vPort bandwidth allocation and metering is performed by the switch and the VFA. In such a case, a bidirectional virtual channel of an assigned bandwidth is established between them for each vPort.
The Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch is connected to top-of-rack aggregator switches, such as RackSwitch G8272 via the 10 GbE external uplink connections. This scenario is illustrated in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Virtual Fabric UFP solution
Converged iSCSI or FCoE network
The Virtual Fabric 10Gb Switch supports Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE), and it can transport iSCSI or FCoE frames.
This switch provides an inexpensive solution for transporting encapsulated FCoE packet to the Fibre Channel Forwarder (FCF), which is functioning as an aggregation switch and an FCoE gateway.
The example scenario with NAS, iSCSI and FCoE storage targets is shown in Figure 4.
Note: For more information about supported FCoE and iSCSI configurations, see the following System Storage Interoperation Center (SSIC) website:
http://ibm.com/systems/support/storage/ssic

Figure 4. Converged network
Related product families
Product families related to this document are the following:
Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
BladeCenter Interoperability Guide
BladeCenter®
NMotion®
RackSwitch
System x®
VMready®
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Hyper-V® is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
